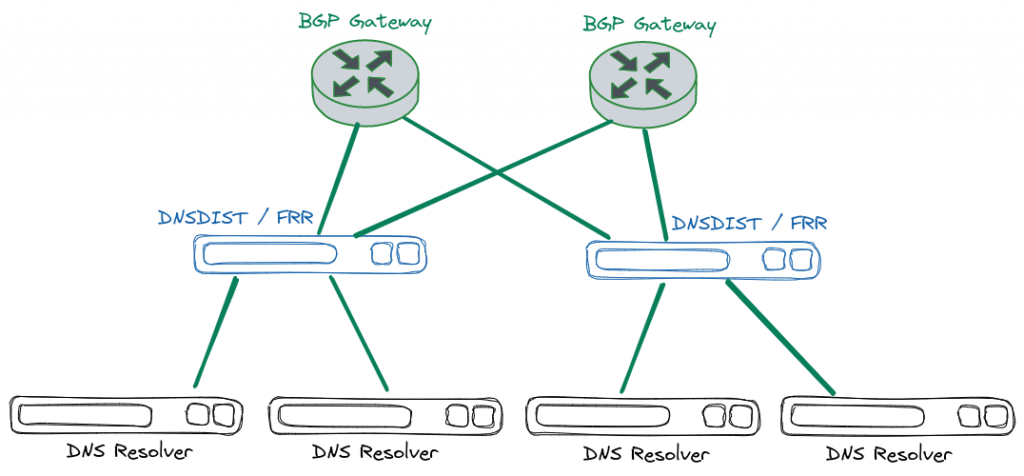
The following guide outlines the deployment methodology and installation instructions for deploying DNS Anycast Infrastructure. The solution comprises of DNS Load Balancers (dnsdist) which sit in front of the Caching DNS Servers and Load Balance the DNS queries among the backend DNS Servers. For advertising the Anycast IPs BGP routing application is used (FRR). For deployment Two CentOS v7.9 servers have been used as the Front End Load Balancers with DNSDIST v1.5.1 and FRR v7.5.
Configuring Anycast IPv4/v6
The IPs used for the Anycast access are configured as loopback IPs on the Load Balancers.
$ cat /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-lo:1 DEVICE=lo:1 IPADDR=11.11.11.11 NETMASK=255.255.255.255 ONBOOT=yes NETWORKING_IPV6=yes DHCPV6C=no IPV6INIT=yes IPV6ADDR=fdcf:5069:ba86:eddd::11/128 $ cat /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-lo:2 DEVICE=lo:2 IPADDR=12.12.12.12 NETMASK=255.255.255.255 ONBOOT=yes
Make sure IPv6 networking and forwarding is enabled for the networks in file /etc/sysconfig/network
NETWORKING_IPV6=yes IPV6FORWARDING=yes
Performance Tuning
Change the sysctl parameters to be able to handle high traffic load.
net.ipv4.conf.all.arp_notify = 1 net.ipv4.conf.all.forwarding=1 net.ipv6.conf.default.disable_ipv6 = 0 net.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6 = 0 net.ipv6.conf.all.forwarding=1 # Disable TCP timestampt net.ipv4.tcp_timestamps=0 # Change the amount of incoming connections and incoming connections backlog net.core.somaxconn=512 net.core.netdev_max_backlog=4096 # Increase the default and maximum send/receive buffers net.core.rmem_default = 16777216 net.core.rmem_max = 16777216 net.core.wmem_default = 16777216 net.core.wmem_max = 16777216 # net.ipv4.ip_local_port_range=16384 60999 # net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_max = 524288 net.nf_conntrack_max = 524288
Increase the Connection Tracking Hash Size in file /etc/modprobe.d/nf_conntrack.conf.
options nf_conntrack expect_hashsize=131072 hashsize=131072
Allow the applications on the server to be able to open large number of file. Edit the file /etc/security/limits.conf and make the following entries.
...... ...... * soft nofile 32768 * hard nofile 32768 ...... ......
Installation of DNSDIST Application
Add the EPEL repository for CentOS 7 and install the dnsdist application. Enable dnsdist to start on boot.
$ sudo yum install epel-release $ sudo yum install yum-plugin-priorities $ sudo curl -o /etc/yum.repos.d/powerdns-dnsdist-15.repo \ https://repo.powerdns.com/repo-files/centos-dnsdist-15.repo $ sudo yum install dnsdist $ sudo systemctl enable dnsdist
Configuration of DNSDIST Application
The configurations need to be done in the configuration file /etc/dnsdist/dnsdist.conf. Create the configuration file and restrict the file access to dnsdist process so that the security keys or credentials are not readable by everyone.
$ sudo touch /etc/dnsdist/dnsdist.conf $ sudo chown dnsdist /etc/dnsdist/dnsdist.conf $ sudo chmod 640 /etc/dnsdist/dnsdist.conf
The dnsdist application provides a command line console over an encrypted tcp connection for controlling it, debugging DNS issues and retrieving statistics. We need to generate the encryption key by starting the application, make the key and put it into the configuration file.
$ dnsdist -l 127.0.0.1:5300
[..]
> makeKey()
setKey("ENCODED KEY")
To configure DNSDIST as load balancer for backend DNS servers, we need to listen on port 53 on IPv4/v6 and both TCP and UDP. To handle large incoming requests we will increase the dnsdist listeners (equal to number of cores). We will restrict the access to the listener to on specific IPs. To protect against Denial of Service Attacks we will restrict the number of queries per IPv4/v6. To provide better response to end users and to take load of the backend servers DNS query caching will be enabled on the load balancers. The application provides a webconsole to view the running server statistics.
-- /etc/dnsdist/dnsdist.conf
controlSocket('127.0.0.1:5199') -- Enable control socket
setConsoleACL('127.0.0.1/32') -- Restrict its access
setKey("ENCODED KEY")
-- Add Listeners, one entry for each CPU Core for v4 and v6
addLocal("0.0.0.0:53", {reusePort=true}) -- Listen on IPv4, port 53
addLocal("0.0.0.0:53", {reusePort=true})
addLocal("0.0.0.0:53", {reusePort=true})
addLocal("0.0.0.0:53", {reusePort=true})
addLocal("[::]:53", {reusePort=true}) -- Listen to IPv6 port 53
addLocal("[::]:53", {reusePort=true})
addLocal("[::]:53", {reusePort=true})
addLocal("[::]:53", {reusePort=true})
-- Backend Servers with weight and QPS limit
newServer({address="20.20.20.3", maxCheckFailures=3, checkInterval=10, weight=5, qps=5000})
newServer({address="20.20.20.4", maxCheckFailures=3, checkInterval=10, weight=5, qps=5000})
newServer({address="30.30.30.3", maxCheckFailures=3, checkInterval=10, weight=5, qps=5000})
newServer({address="30.30.30.4", maxCheckFailures=3, checkInterval=10, weight=5, qps=5000})
-- Allow clients IPs to connect
addACL("10.0.0.0/8")
addACL("172.16.0.0/12")
addACL("192.168.0.0/16")
-- Limit /32 ipv4 and /128 ipv6 to 50 (burst10) /100 (burst20) QPS
addAction(MaxQPSIPRule(50,32,128,10), DelayAction(500))
addAction(MaxQPSIPRule(100,32,128,20), DropAction())
-- Backend server load balancing policy
setServerPolicy(leastOutstanding)
-- Enable DNS query caching
-- 100K entries with avg 512B would take about 50MB of RAM
pc = newPacketCache(100000, {maxTTL=86400, minTTL=0, temporaryFailureTTL=60, staleTTL=60, dontAge=false})
getPool(""):setCache(pc)
-- Enable Webserver
webserver("0.0.0.0:8083", "PASSWORD", "APIKEY", {}, "10.10.10.0/27, 192.168.20.0/27")
Working with DNSDIST Console
The dnsdist application can be accessed via web interface and command line console. The web interface (http://server-ip:8083) displays the running servers statistics. Configuration changes can be done on live server and statistics can be viewed via command console.
$ sudo dnsdist -c
> showVersion()
dnsdist 1.3.3
> showServers()
# Name Address State Qps Qlim Ord Wt Queries Drops Drate Lat Outstanding Pools
0 10.10.10.3:53 up 0.0 5000 1 5 250597 2877 0.0 30.3 0
1 10.10.10.4:53 up 14.9 5000 1 5 877556 4295 0.0 9.8 0
2 20.20.20.3:53 up 4.0 5000 1 5 376735 3108 0.0 20.0 0
3 20.20.20.4:53 up 0.0 5000 1 5 46650 113 0.0 141.0 0
All 17.0 1551538 10393
> getPool(""):getCache():printStats()
Entries: 3923/10000
Hits: 2671621
Misses: 1273977
Deferred inserts: 35
Deferred lookups: 64
Lookup Collisions: 1
Insert Collisions: 1
TTL Too Shorts: 0
> topClients(20)
1 1.2.3.4 579 5.8%
2 20.30.40.18 567 5.7%
3 30.40.20.150 353 3.5%
4 10.10.20.13 312 3.1%
5 10.20.30.50 227 2.3%
21 Rest 5574 55.7%
> topQueries(10)
1 a.root-servers.net. 1142 11.4%
2 graph.facebook.com. 302 3.0%
3 www.google.com. 170 1.7%
4 connectivitycheck.gstatic.com. 141 1.4%
5 graph.instagram.com. 108 1.1%
6 googleads.g.doubleclick.net. 104 1.0%
7 www.googleapis.com. 97 1.0%
8 video.fisb1-1.fna.fbcdn.net. 96 1.0%
9 scontent.fisb1-2.fna.fbcdn.net. 95 0.9%
10 youtubei.googleapis.com. 94 0.9%
11 Rest 7651 76.5%
> showResponseLatency()
Average response latency: 22.26 msec
msec
0.10
0.20
0.40 .
0.80 **********************************************************************
1.60 ****
3.20 *
6.40 .
12.80 .
25.60 :
51.20 ***
102.40 *
204.80 ****
409.60 *
819.20 :
1638.40 .
> showRules()
# Matches Rule Action
0 3 IP (/32, /128) match for QPS over 80 burst 20 drop
1 15743 IP (/32, /128) match for QPS over 40 burst 10 delay by 500 msec
>
Installation of FRR Application
Add the FRR repository for CentOS 7 and install the application.
$ curl -O https://rpm.frrouting.org/repo/frr-stable-repo-1-0.el7.noarch.rpm $ sudo yum install ./frr-stable-repo-1-0.el7.noarch.rpm $ sudo yum install frr frr-pythontools
Enable the BGP routing daemon and VTY shell in the file /etc/frr/daemons.
... ... bgpd=yes ... ... ... vtysh_enable=yes ... ...
Configure the frr service to be dependent on the dnsdist application. In case the dnsdist process dies the routing of the anycast from that node should also stop. Edit the file /usr/lib/systemd/system/frr.service and enter the highlighted dependency.
... [Unit] Description=FRRouting Documentation=https://frrouting.readthedocs.io/en/latest/setup.html Wants=network.target Requires=dnsdist.service ...
Restart the systemctl daemon to enable the change. Enable the frr damon to start on bootup.
$ sudo systemctl daemon-reload $ sudo systemctl enable frr $ sudo systemctl start frr
Configure BGP Routing
The Anycast route will be advertised from the Load Balancers using BGP. The Anycast IP will be configured as loopback IP and this will be the only allowed IP to be advertised.
$ vtysh Hello, this is FRRouting (version 7.5). Copyright 1996-2005 Kunihiro Ishiguro, et al. dnslb.domain.com# sh running-config Building configuration... Current configuration: ! frr version 7.5 frr defaults datacenter hostname dnslb.domain.com log file /var/log/frr/frr.log informational service password-encryption ! password 8 XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX enable password 8 XXXXXXXXXXXX ! router bgp 64520 bgp router-id machine-ip-address neighbor bgp-ipv4-peer-1 remote-as 123456 neighbor bgp-ipv4-peer-1 ebgp-multihop 255 neighbor bgp-ipv4-peer-2 remote-as 123456 neighbor bgp-ipv4-peer-2 ebgp-multihop 255 neighbor bgp-ipv6-peer-1 remote-as 123456 neighbor bgp-ipv6-peer-1 interface eth0 neighbor bgp-ipv6-peer-1 ebgp-multihop 255 neighbor bgp-ipv6-peer-2 remote-as 123456 neighbor bgp-ipv6-peer-2 interface eth0 neighbor bgp-ipv6-peer-2 ebgp-multihop 255 ! address-family ipv4 unicast redistribute connected neighbor bgp-ipv4-peer-1 soft-reconfiguration inbound neighbor bgp-ipv4-peer-1 route-map DNS-LB-v4 in neighbor bgp-ipv4-peer-1 route-map DNS-LB-v4 out neighbor bgp-ipv4-peer-2 soft-reconfiguration inbound neighbor bgp-ipv4-peer-2 route-map DNS-LB-v4 in neighbor bgp-ipv4-peer-2 route-map DNS-LB-v4 out exit-address-family ! address-family ipv6 unicast redistribute connected neighbor bgp-ipv6-peer-1 activate neighbor bgp-ipv6-peer-1 soft-reconfiguration inbound neighbor bgp-ipv6-peer-1 route-map ANY-IPv6 in neighbor bgp-ipv6-peer-1 route-map DNS-LB-V6 out neighbor bgp-ipv6-peer-2 activate neighbor bgp-ipv6-peer-2 soft-reconfiguration inbound neighbor bgp-ipv6-peer-2 route-map ANY-IPv6 in neighbor bgp-ipv6-peer-2 route-map DNS-LB-V6 out exit-address-family ! ip prefix-list ANY seq 5 deny 0.0.0.0/0 le 32 ip prefix-list DNS-LB-v4 seq 30 permit 11.11.11.11/32 ip prefix-list DNS-LB-v4-secondary seq 30 permit 12.12.12.12/32 ! ipv6 prefix-list DNS-LB-v6 seq 10 permit fdcf:5069:ba86:eddd::11/128 ipv6 prefix-list ANY-IPv6 seq 5 permit ::/0 le 128 ! route-map DNS-LB-v4 permit 10 match ip address prefix-list DNS-LB-v4 ! route-map DNS-LB-v4 permit 20 match ip address prefix-list DNS-LB-v4-secondary set as-path prepend 64520 64520 ! route-map DNS-LB-V6 permit 10 match ipv6 address prefix-list DNS-LB-v6 ! route-map ANY-IPv6 permit 10 match ipv6 address prefix-list ANY-IPv6 ! line vty ! end
References
https://rpm.frrouting.org/
https://making.pusher.com/per-ip-rate-limiting-with-iptables/
https://berthub.eu/tmp/dnsdist-md/dnsdist-diagrams.md.html
https://dnsdist.org/quickstart.html
https://dnsdist.org/reference/config.html
https://ripe74.ripe.net/presentations/122-PLexis-dnsdist-lightning.pdf
